Develop a Hypothesis
Assumptions
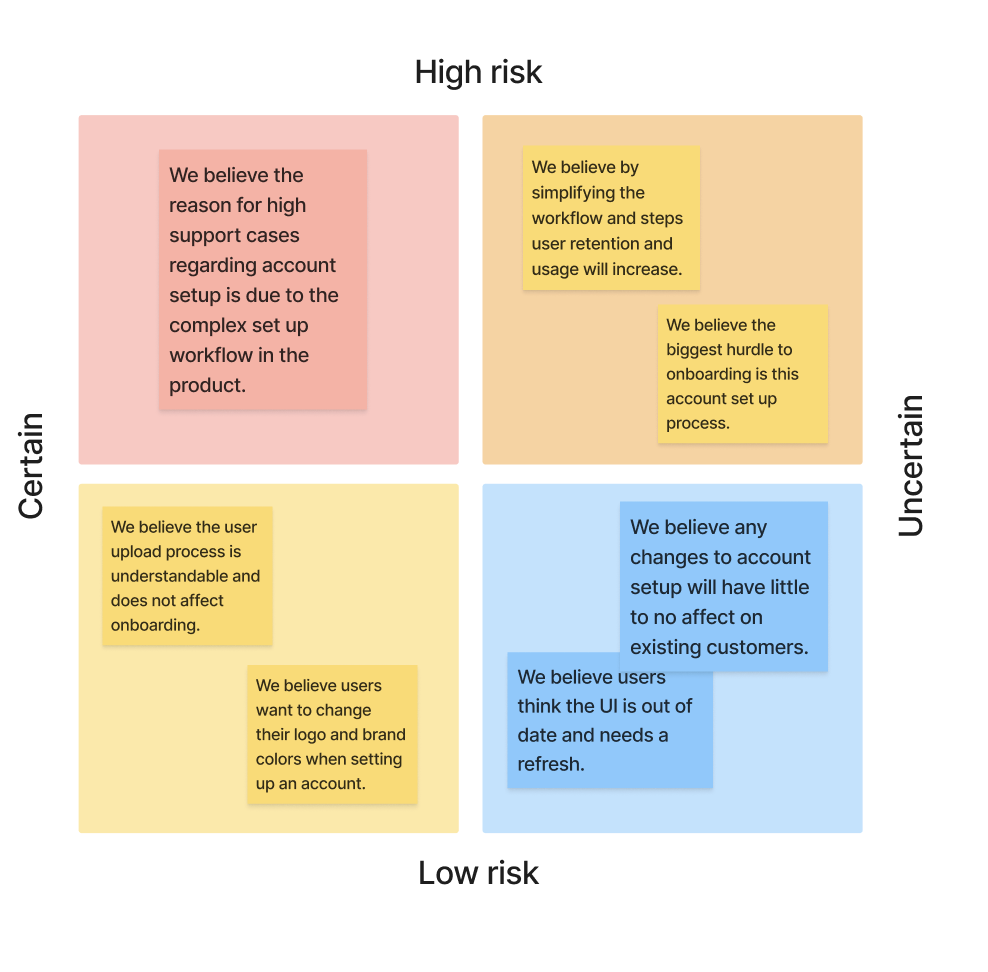
I often hear stakeholders say, "Most customers want this." Typically, this phrase is based on anecdotal customer conversations. While these are valid, it's important to note the difference between an assumption or hypothesis and data. For this purpose, I find using assumption mapping and hypothesis building helpful.

Discover
User Interviews
It is essential to talk directly with users to understand their wants and needs. User interviews are a vital technique for asking users to describe experiences and for documenting the helpful and unhelpful things in their day-to-day interactions with the product. A technique I frequently use is to ask users to rank those unhelpful things on a scale of 1-5. This ranking allows me to identify the most painful areas for customers quickly.


Customer Feedback
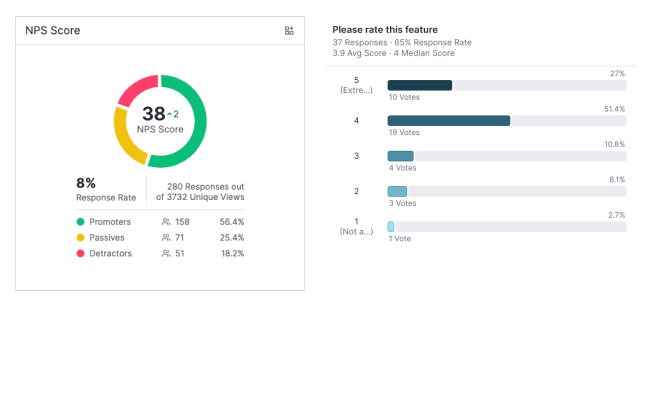
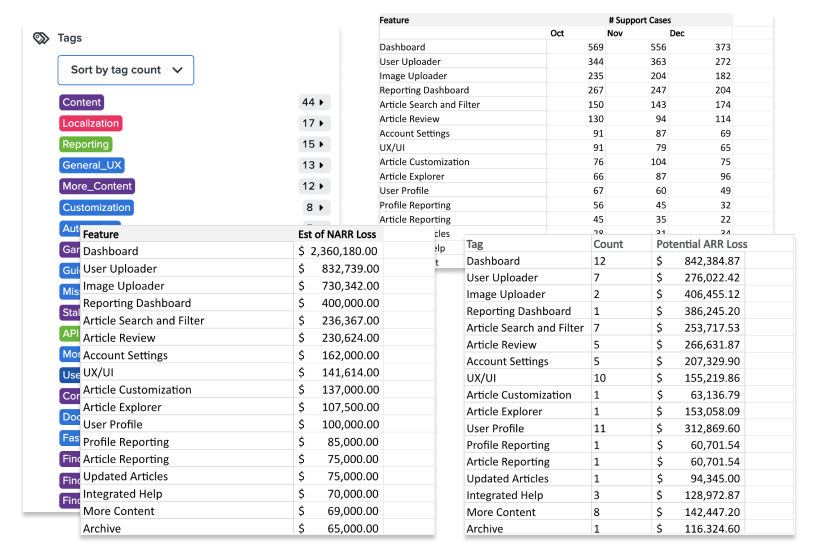
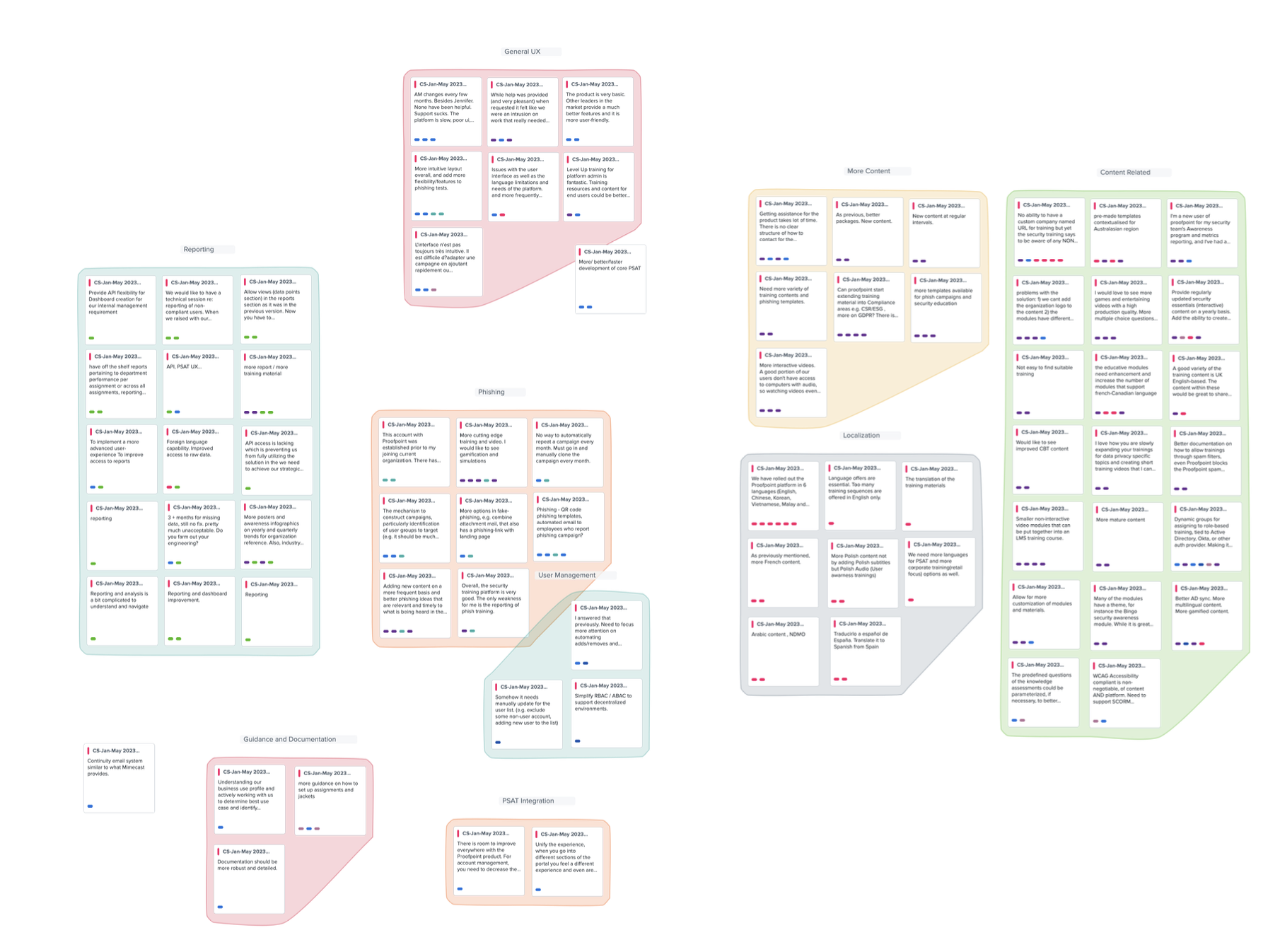
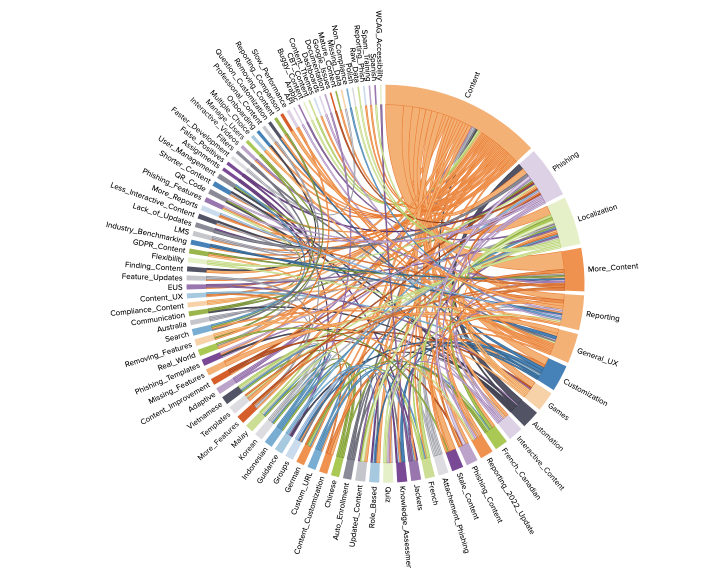
Collecting ongoing customer feedback through tools like NPS and Customer Satisfaction ratings is extremely helpful in maintaining a steady stream of customer engagement around product issues. I typically tag input and break it into affinity categories or chord diagrams. This provides me with a way to quantify qualitative data so the organization can identify the problem areas customers complain about most frequently. I find it helpful to break tags down by revenue risk and support issues to tie the customer ask back to business value. Many UX tools now utilize Gen AI to accomplish what was previously a manual task very quickly.
Surveys
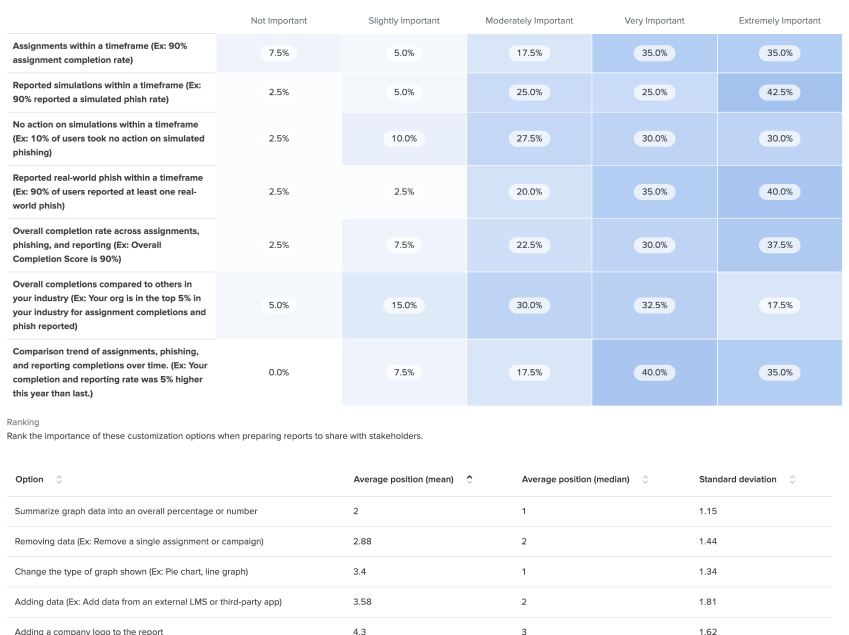
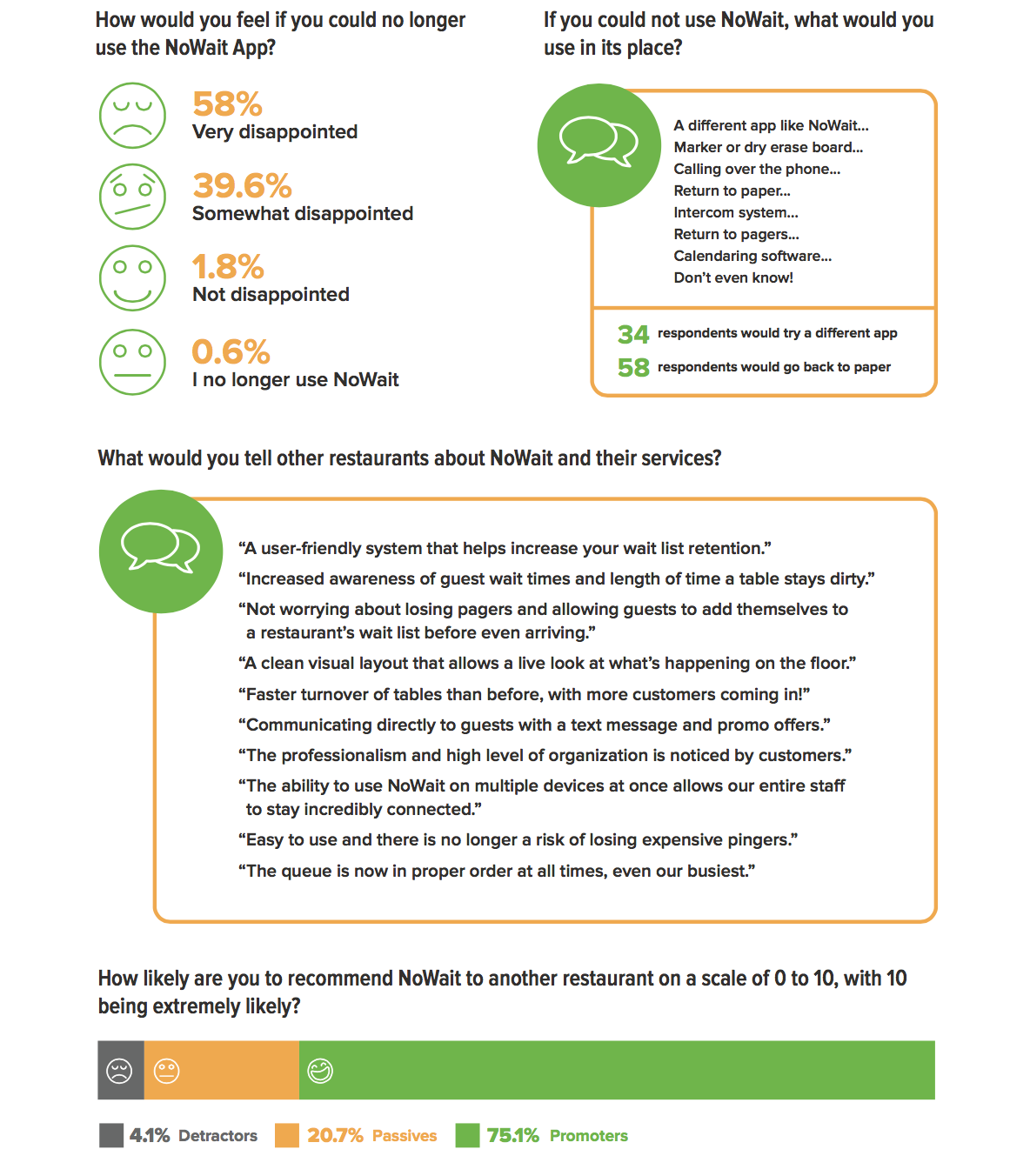
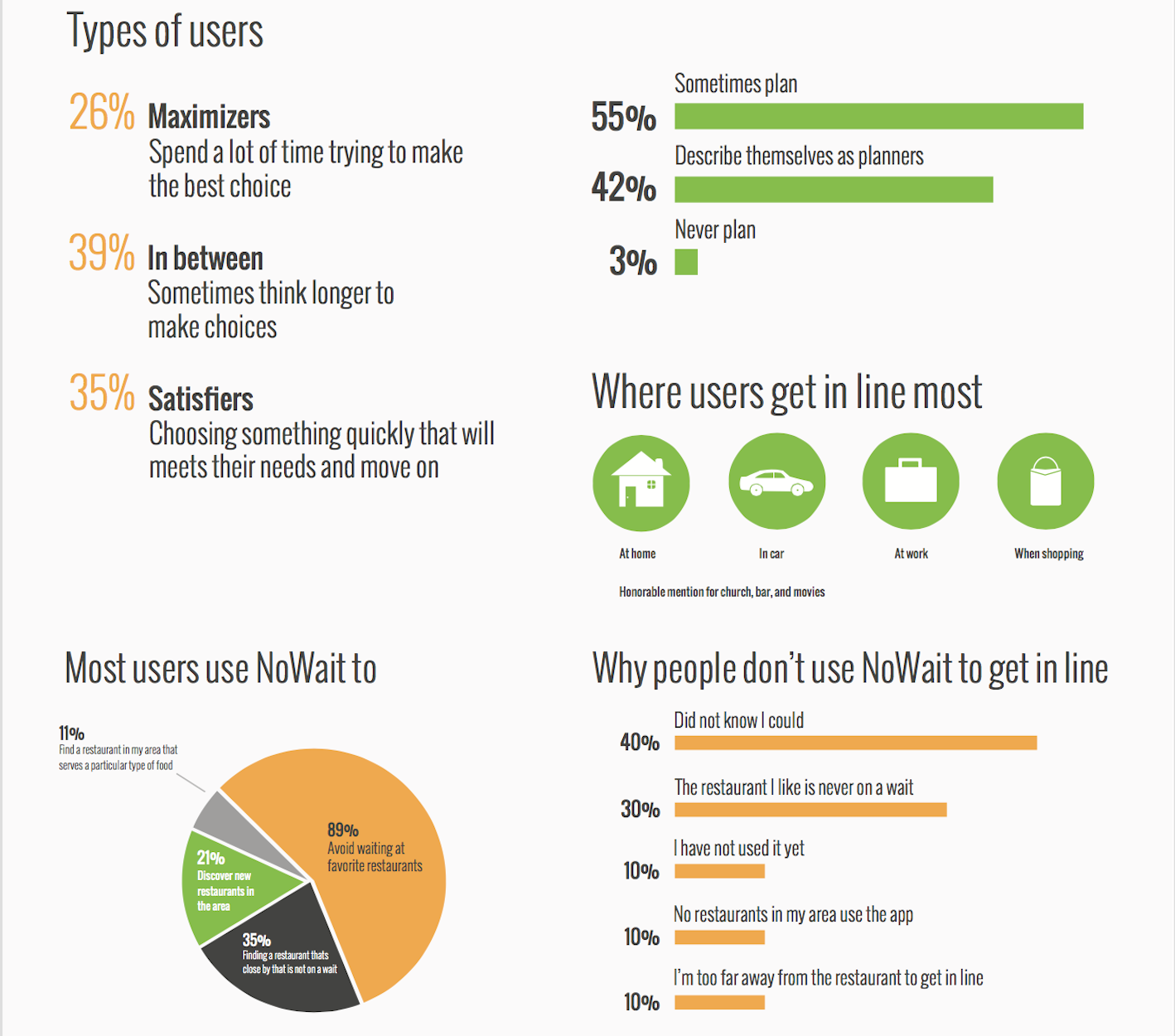
If I have customer feedback or user interview results, following up by quantifying those findings is helpful. Customer surveys are a great tool to accomplish this. Through surveys, I can identify typical customer jobs, customer satisfaction with the product, their day-to-day behavior, and demographic information.
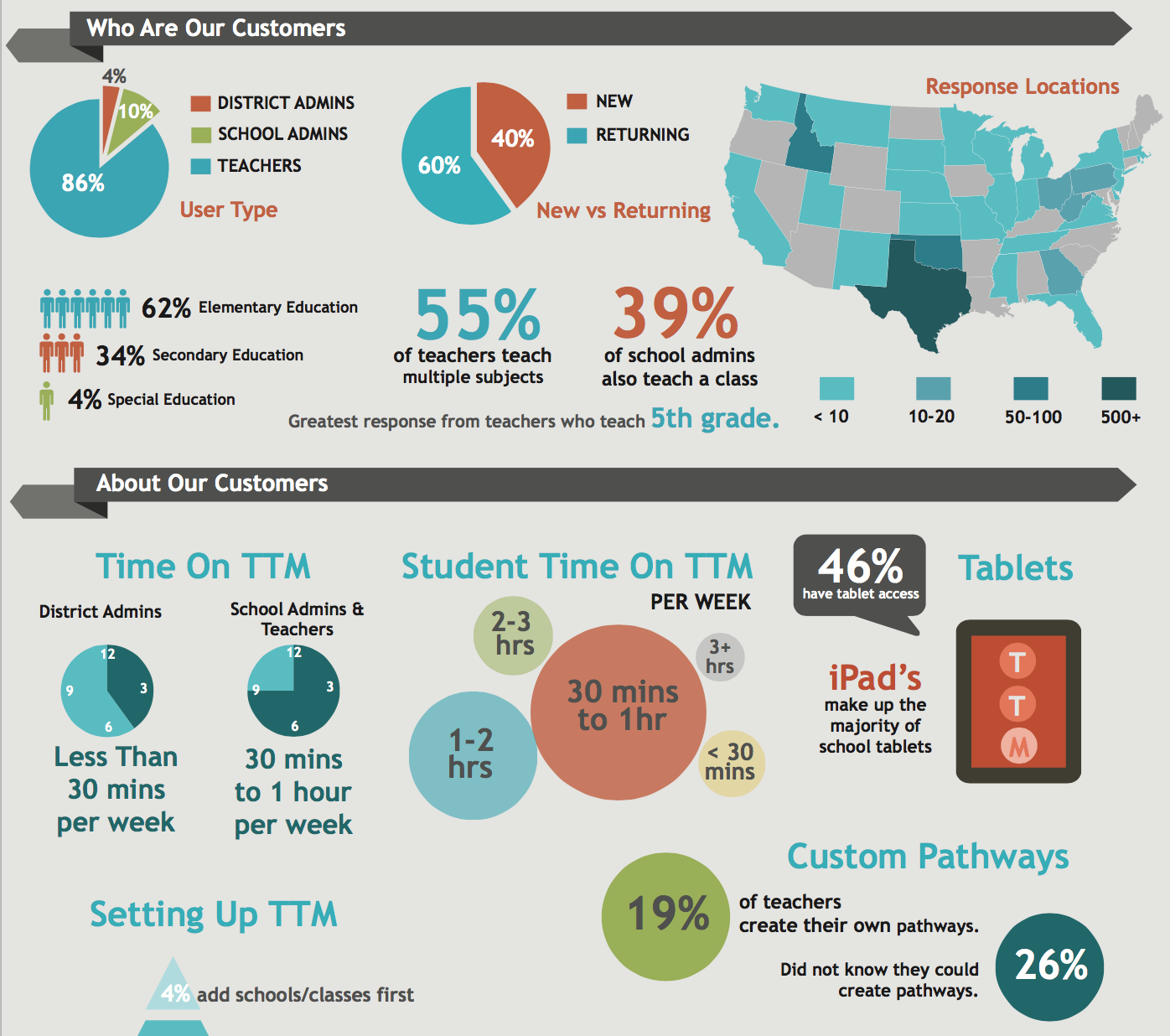
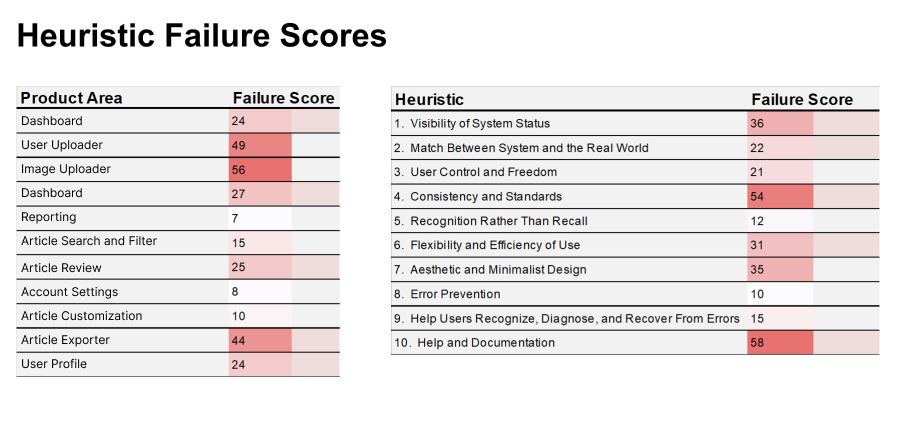
Heuristic Review and Competitor Analysis
Heuristic reviews are a very low-stakes way of identifying pain points. These will not help you understand customer problems, but they can locate some low-hanging issues that could improve compared to best practices.
Though I consider UX to be focused primarily on customer retention, it is crucial to understand what competitors are doing in your market and where your product is falling short. Investigating competitor product offerings and developing a comparison can help focus on the features that are not just user pain points but competitive differentiators.
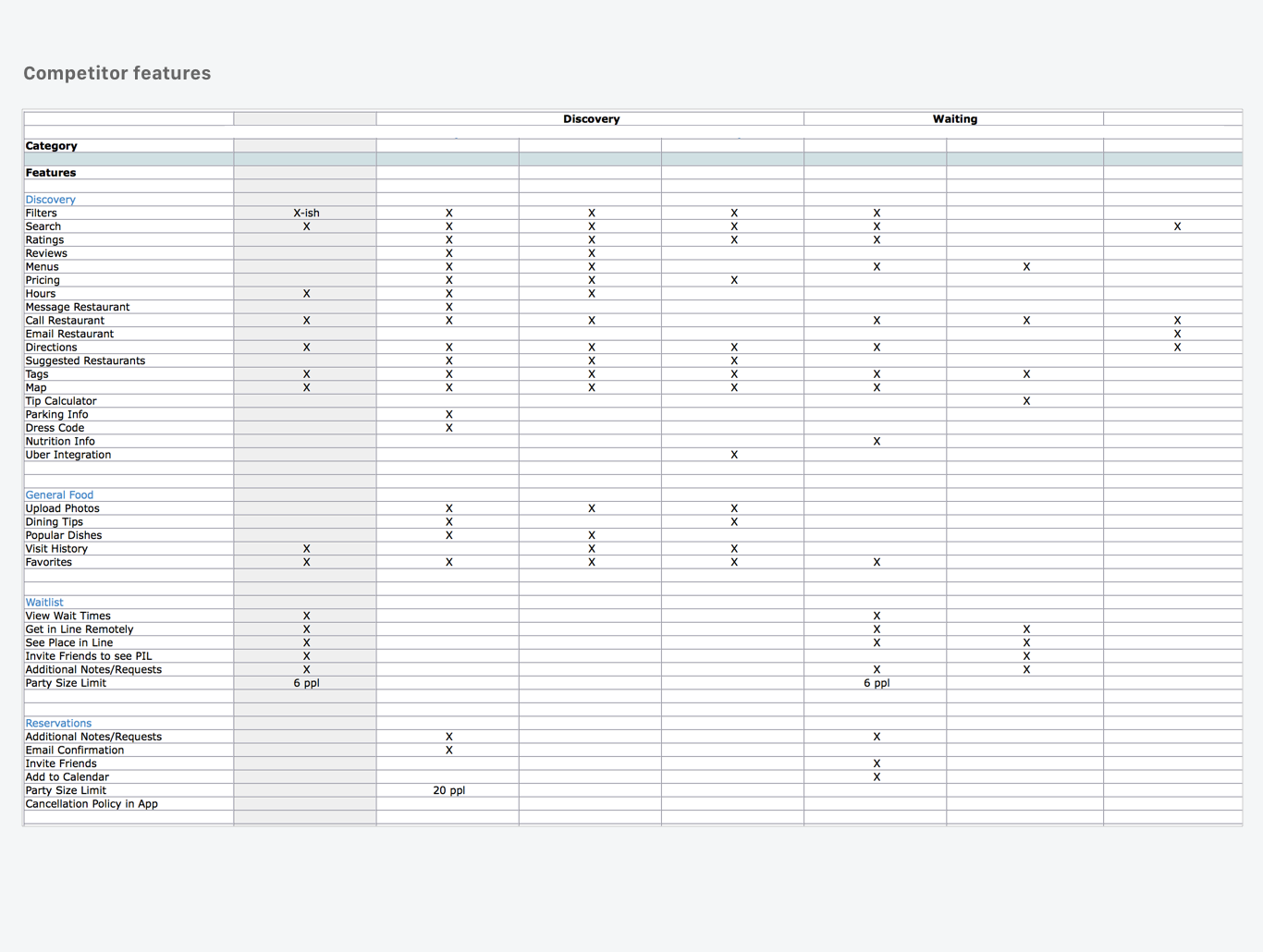
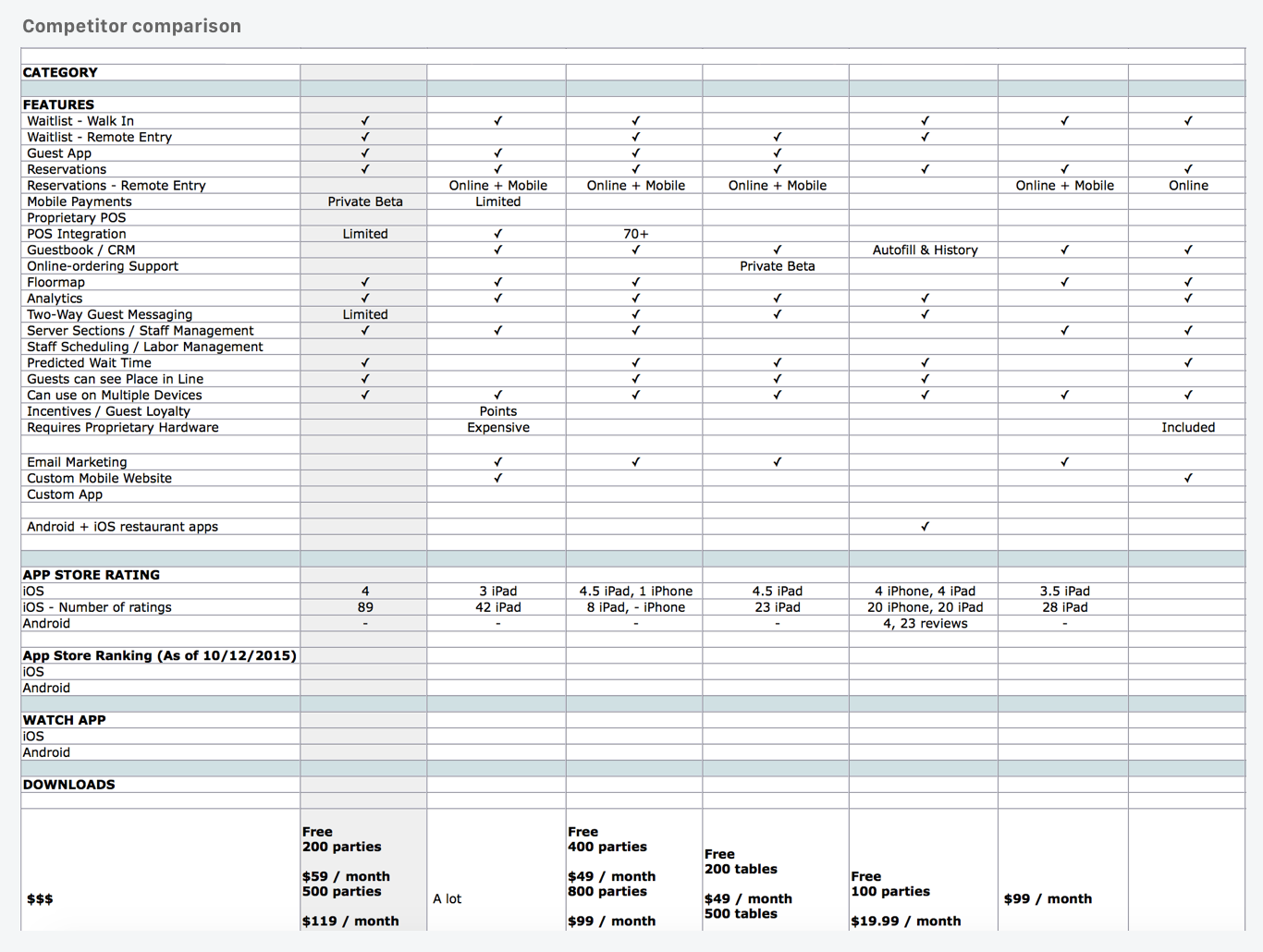
Define
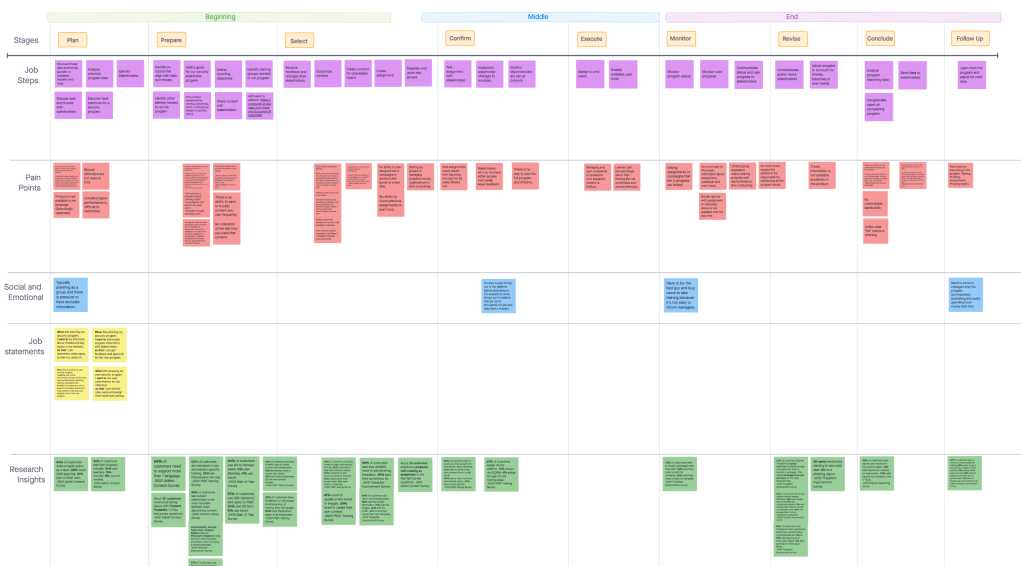
Customer Journey & Personas
Customer Journeys and Job Maps are a fantastic way to help keep the big picture of your user's interactions with your product in mind. Many organizations fall victim to silos based on product areas, and these can help keep everyone aligned on the overall jobs of a typical customer.
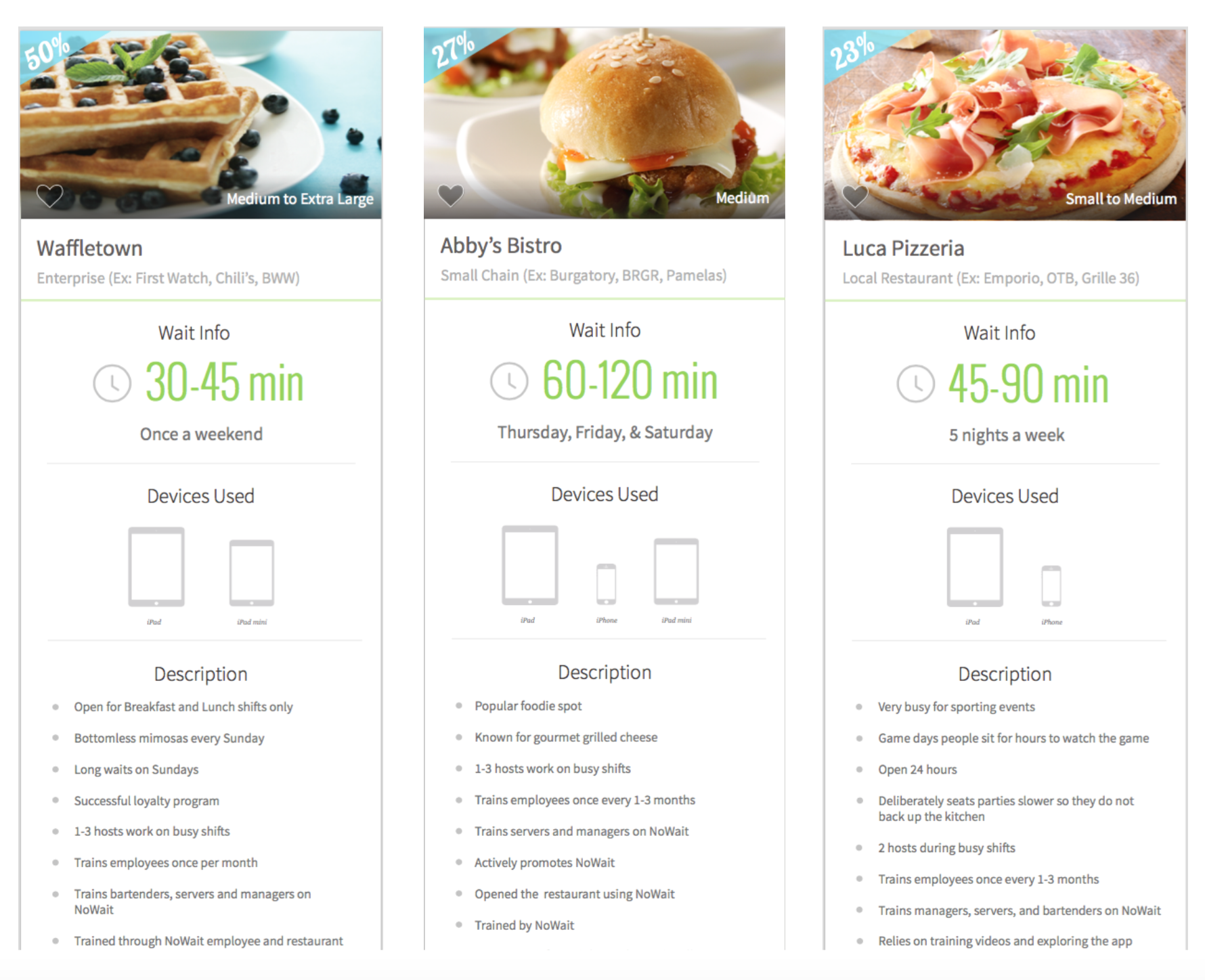
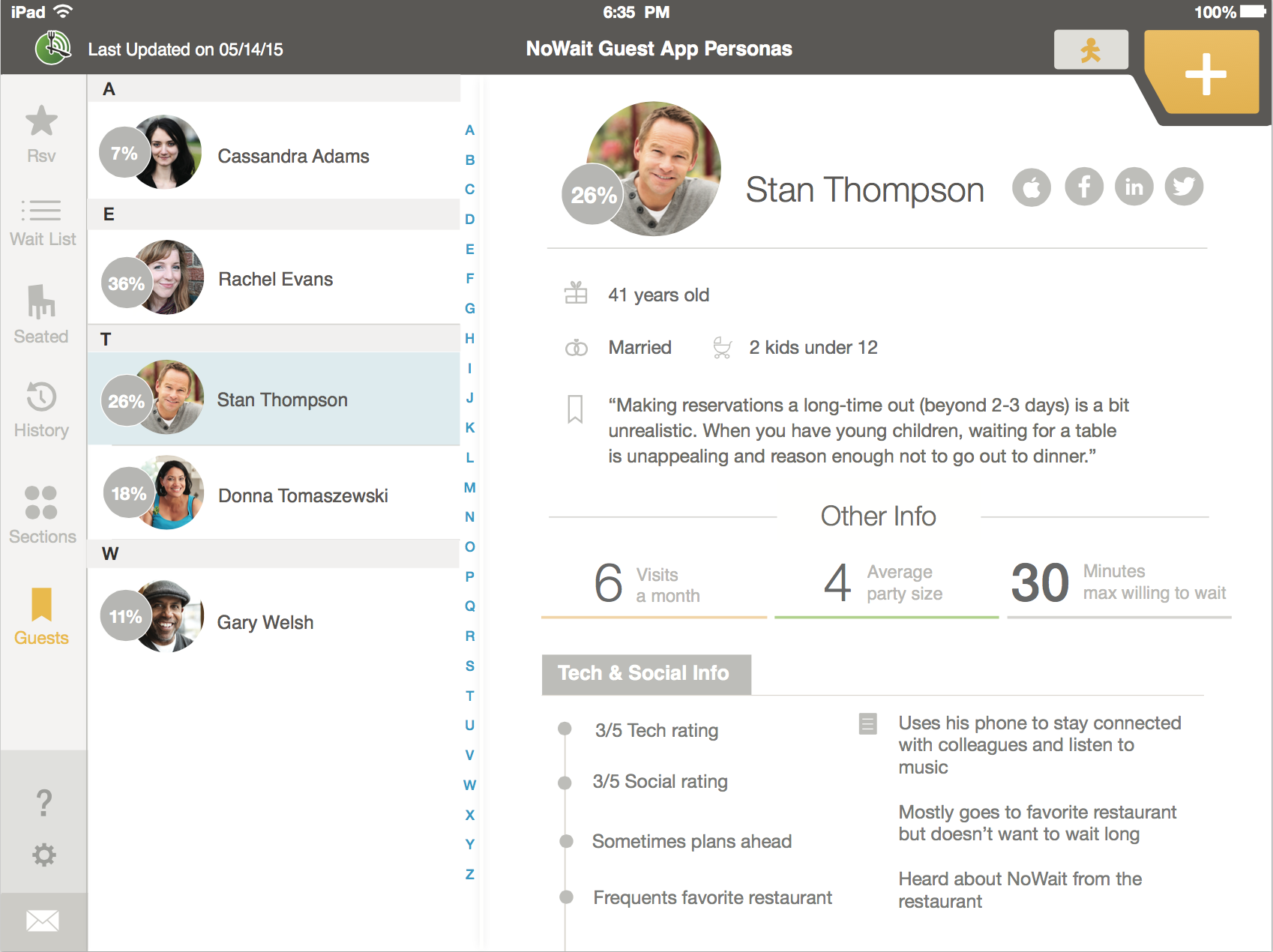
Personas are a bit misunderstood. These can be helpful to create empathy with your organization. The goal is to create a face for a typical user group to help people identify with and relate to.



Goal and Problem Definition
Once the team understands customer needs and use cases, we can establish a customer job or business goal to narrow our focus. We will then determine the success metrics and scope of the project.
Once we have determined the goals, success metrics, and scope, we can brainstorm solutions for the problem. The last step would be to determine the remaining unknowns and how risky they are to the project's success. The riskiest items will need additional research.


Concepts
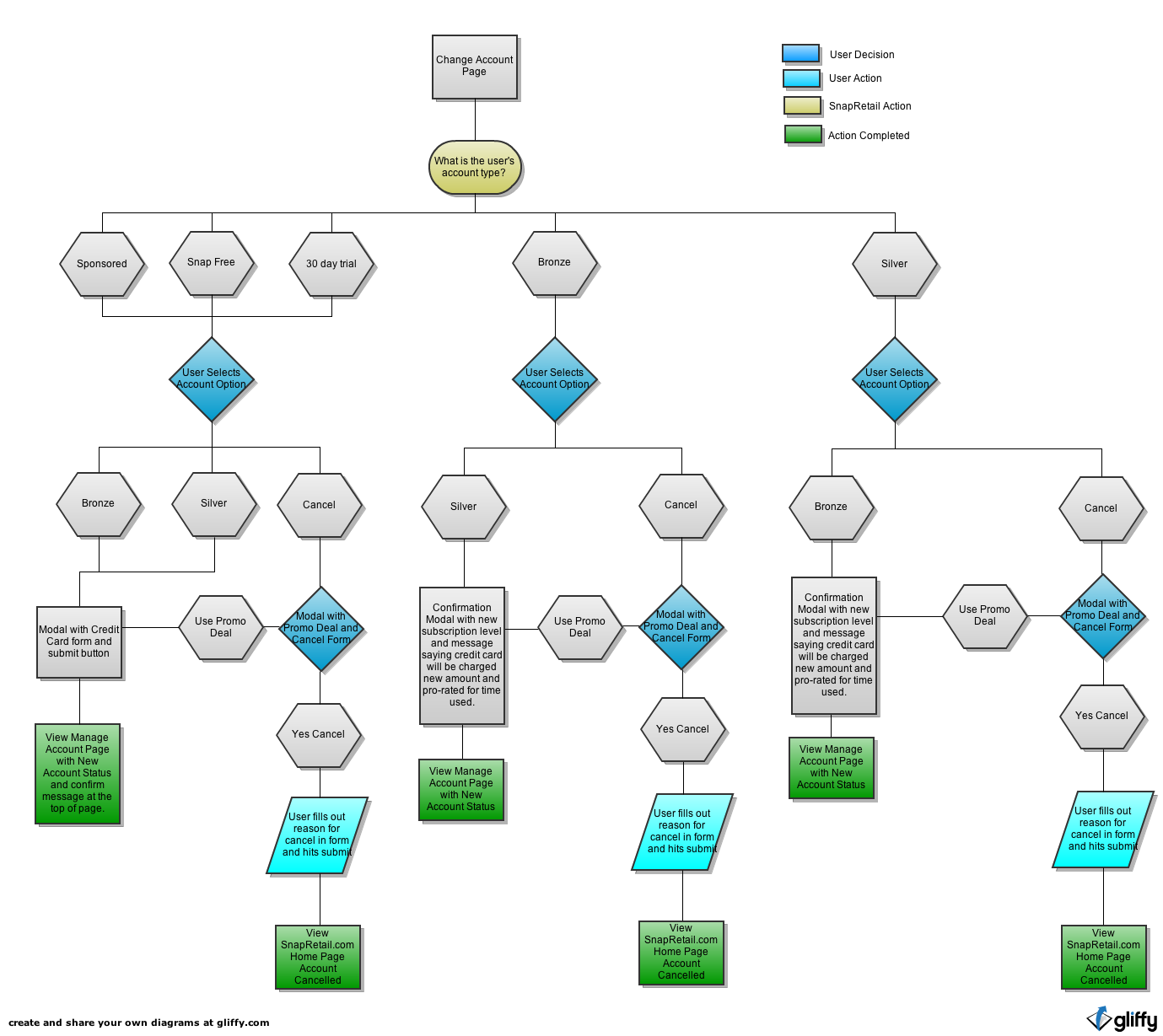
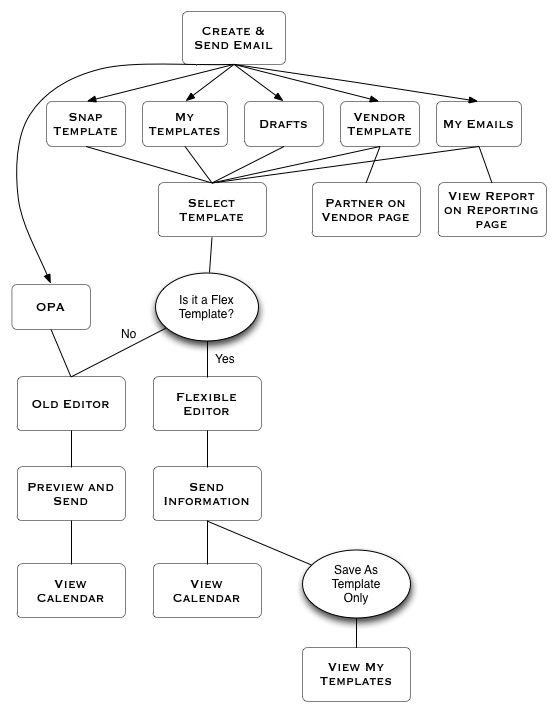
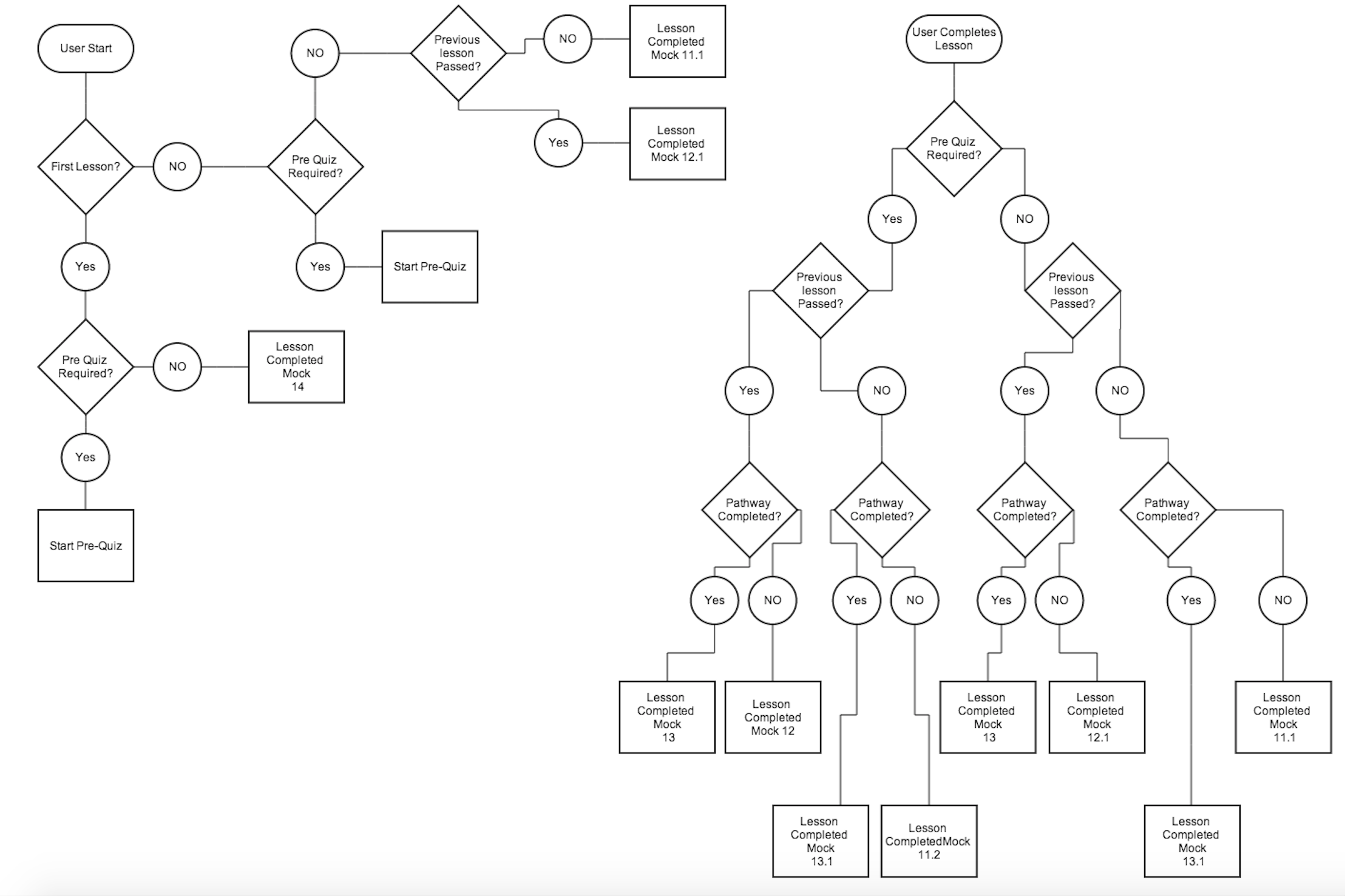
Flowcharts
When building complicated, complex, multiple-team projects, it's helpful to diagram out the flow and interactions at each stage. Flowcharts allow me to discuss the features and interactions without stakeholders getting caught up in UI designs.
Wireframes, Concepts, Prototypes
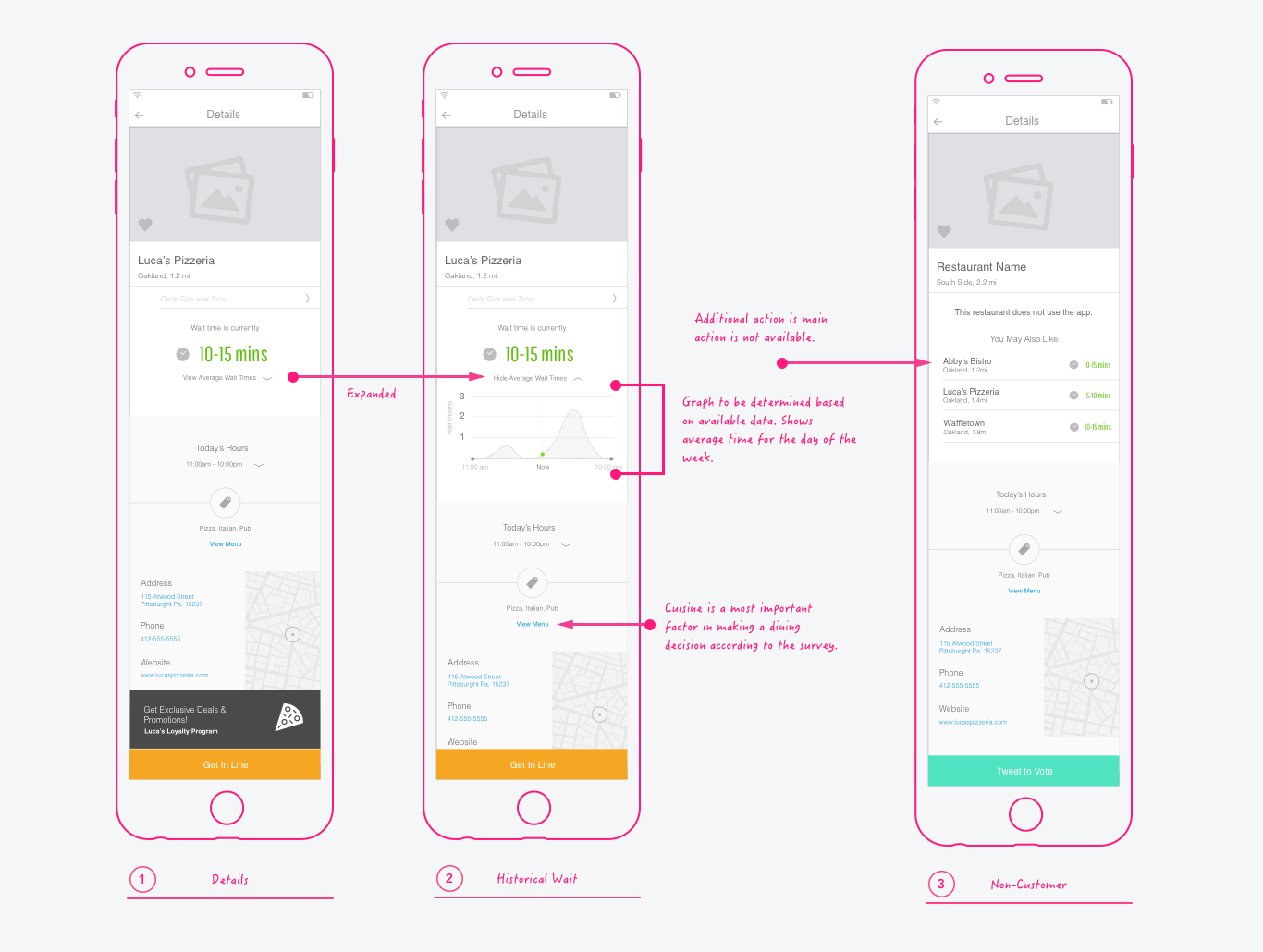
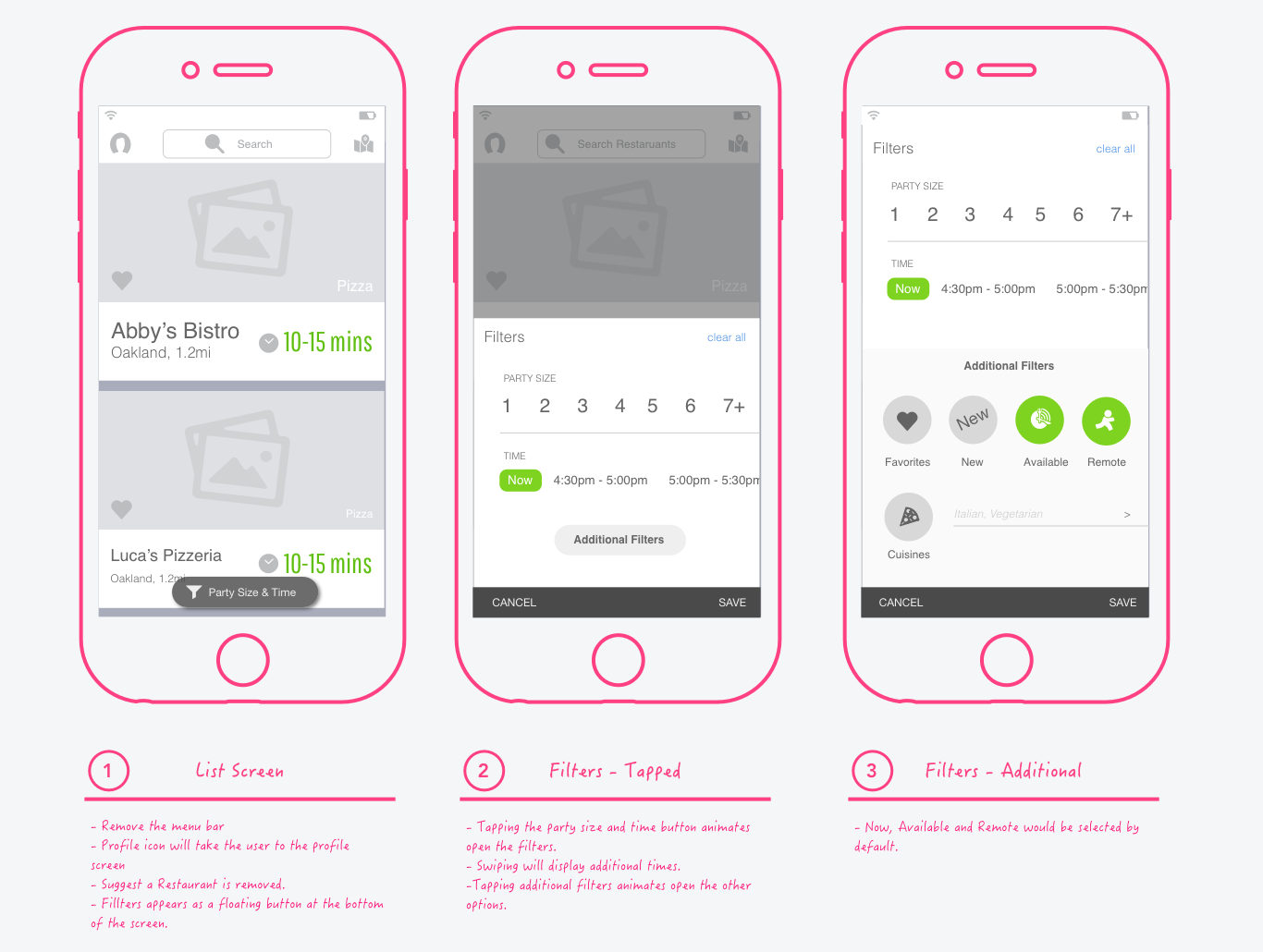
Creating clickable prototypes for sharing feature interactions with stakeholders and user testing with customers is beneficial. This helps the team to get alignment on the full scope of the feature and make adjustments.
Wireframes are typically helpful if UI is getting in the way of discussions. Wireframes are generally unnecessary for most organizations with a standardized style repository.
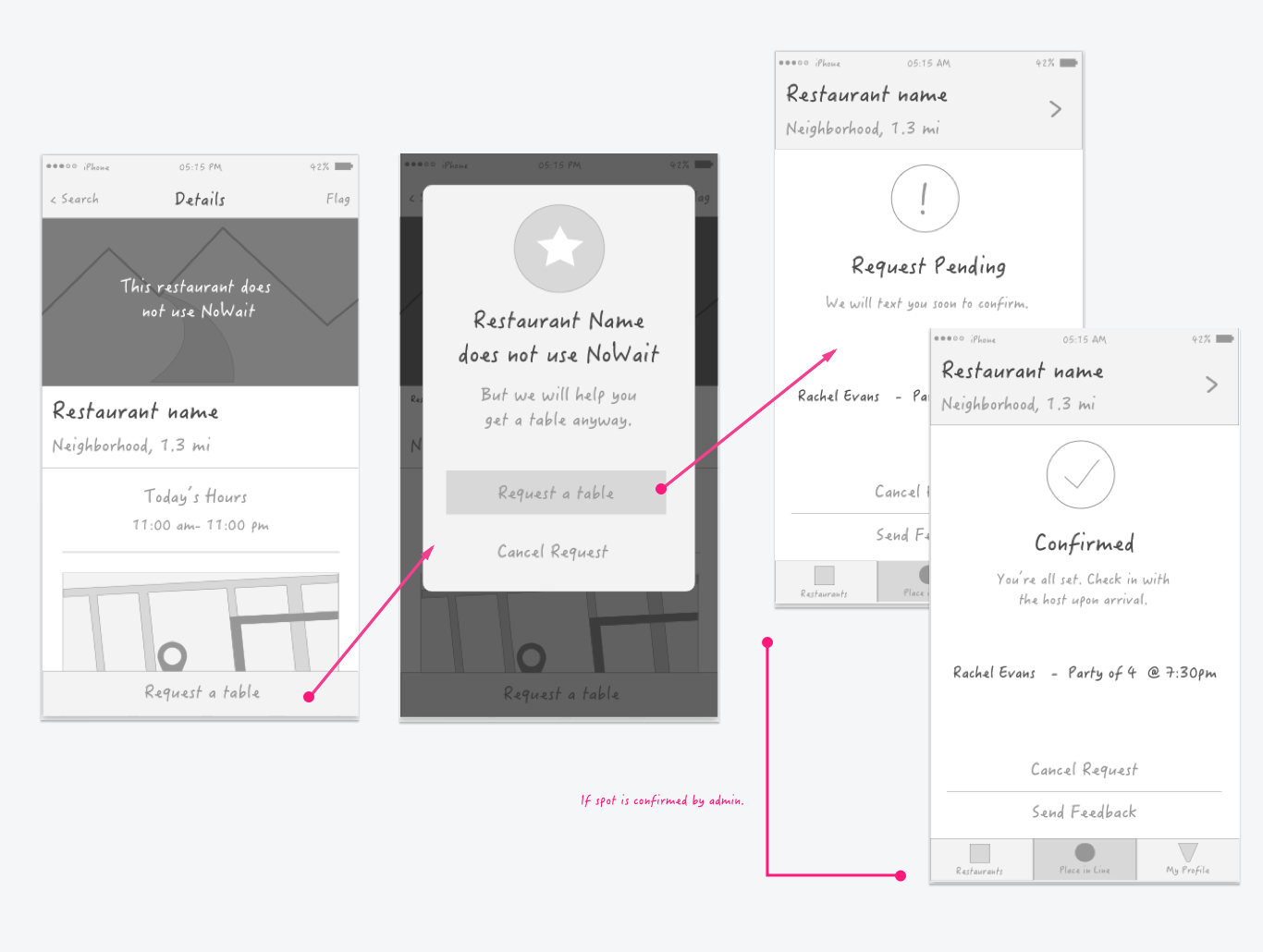
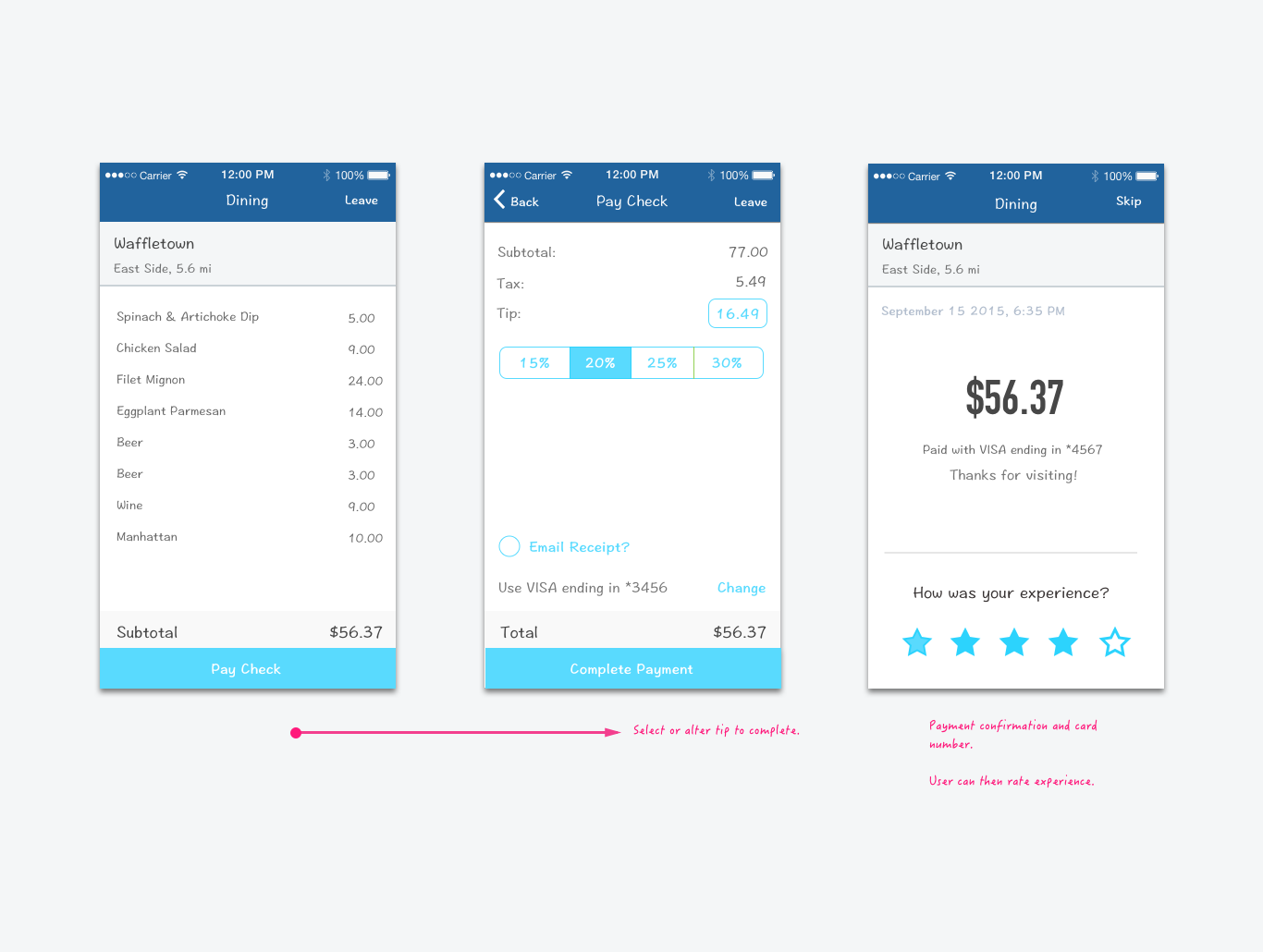
Usability Tests
Putting concepts in front of users as often as possible is essential. I do this through user tests and prototypes. I've had great success running moderated user tests via screen share. Moderated tests have allowed me to ask follow-up questions and gain insights that I would not have learned using an unmoderated tool. However, I have sometimes used tools like Usability Hub and Optimal Workshop to conduct unmoderated tests for more minor features or for time-saving reasons.


Measure and Learn
Evaluate Goals and Iterate
Once a project is generally available to customers, the UX team must track the results based on the goals established and share those with stakeholders. Measuring success helps the organization to understand where we could have done better on a feature and brainstorm ideas to get the project back on track to meet the goals.
